Mastering personal finance is a crucial skill for securing long-term success and financial independence. Whether you’re just starting your financial journey or looking to optimize your existing strategy, understanding the fundamentals and applying them consistently can set you on a path to financial freedom. In this article, we’ll explore key concepts and actionable steps you can take to master personal finance and achieve lasting success.
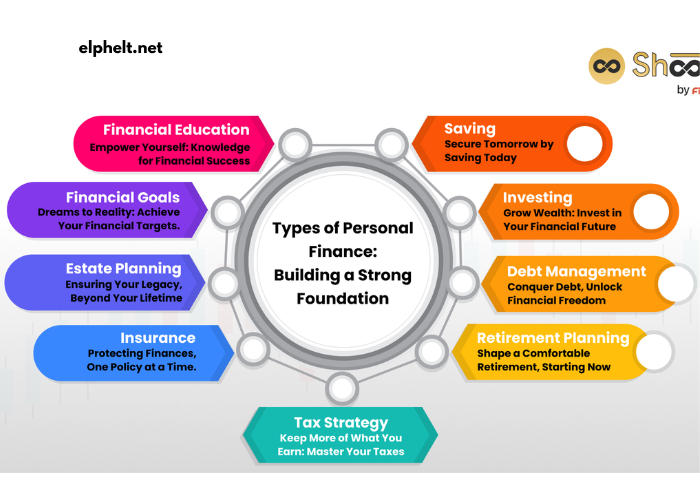
Understanding Personal Finance
Personal finance encompasses everything related to managing your money, from budgeting and saving to investing and planning for retirement. It involves making smart decisions about how to spend, save, and invest your money in a way that supports your long-term goals.
The Basics of Personal Finance
At its core, personal finance involves the following key areas:
- Income Management: This is about understanding where your money comes from and ensuring you’re maximizing your earning potential through career advancement, side hustles, or investments.
- Spending and Budgeting: Tracking your expenses and creating a budget is essential for controlling your financial situation. By knowing where your money is going, you can prioritize important expenses and cut back on unnecessary spending.
- Saving and Emergency Funds: Building up a savings cushion is vital for unexpected expenses and peace of mind. An emergency fund should cover at least 3 to 6 months of living expenses.
- Debt Management: Managing and paying off debt efficiently is key to financial success. Understanding good vs. bad debt, interest rates, and repayment strategies is crucial for avoiding financial pitfalls.
- Investing for the Future: Investing your money wisely allows you to build wealth over time. This can include stocks, bonds, mutual funds, real estate, and retirement accounts like 401(k)s or IRAs.
- Retirement Planning: Preparing for retirement ensures you have enough funds to live comfortably in your later years. This involves saving, investing, and understanding your retirement needs and goals.
Setting Financial Goals
Before diving into managing your finances, it’s essential to set clear and realistic financial goals. These goals will provide you with direction and motivation, helping you stay focused on your long-term success.
SMART Goals
A well-established method for goal-setting is the SMART criteria, which ensures that your financial goals are:
- Specific: Clearly define what you want to achieve (e.g., save $10,000 for a down payment).
- Measurable: Make sure you can track your progress (e.g., save $500 per month).
- Achievable: Set realistic goals based on your current income and expenses.
- Relevant: Choose goals that align with your values and long-term vision.
- Time-bound: Set deadlines to keep yourself on track (e.g., save $10,000 in 12 months).
By using SMART goals, you can break down larger, more intimidating financial objectives into manageable steps, making it easier to achieve them.
Building a Solid Budget
One of the most fundamental aspects of mastering personal finance is creating and sticking to a budget. A well-planned budget helps you track your income, expenses, and savings, ensuring that you’re in control of your financial situation.
Steps to Create a Budget
- Assess Your Income: Begin by calculating all your sources of income, including your salary, freelance earnings, side gigs, and passive income streams.
- Track Your Expenses: List all of your monthly expenses, from rent and utilities to groceries and entertainment. Don’t forget annual or irregular expenses like insurance premiums or holiday shopping.
- Categorize Your Spending: Break your expenses into categories such as fixed (e.g., rent, utilities) and variable (e.g., groceries, entertainment). This will help you identify areas where you can cut back.
- Set Spending Limits: Based on your income and goals, set spending limits for each category. Allocate a portion of your income to savings, debt repayment, and investing.
- Monitor and Adjust: Regularly review your budget to ensure you’re staying on track. Life changes, so adjust your budget as needed to accommodate new circumstances.
The 50/30/20 Rule
A simple and effective budgeting method is the 50/30/20 rule, which suggests allocating:
- 50% of your income to needs (housing, utilities, transportation).
- 30% to wants (entertainment, dining out, travel).
- 20% to savings and debt repayment.
By following this rule, you can maintain a balanced approach to your finances while still prioritizing saving and reducing debt.
Saving for the Future
Building savings is a critical step in mastering personal finance. Saving allows you to handle unexpected expenses, achieve your financial goals, and eventually create wealth.
Creating an Emergency Fund
An emergency fund is essential for covering unexpected costs, such as medical bills, car repairs, or job loss. Having this financial cushion will give you peace of mind and prevent you from falling into debt during difficult times.
To create an emergency fund, aim to save at least 3 to 6 months’ worth of living expenses. Start small, if necessary, and gradually increase your savings over time. Keep this fund in a high-yield savings account or money market account to earn some interest while ensuring liquidity.
Short-Term and Long-Term Savings Goals
In addition to an emergency fund, you should also set aside money for short-term and long-term goals. For short-term goals, such as purchasing a new car or going on a vacation, open a dedicated savings account and contribute regularly.
For long-term goals, such as retirement or buying a home, invest in growth-oriented vehicles like stocks, bonds, or retirement accounts. The earlier you start saving and investing for these goals, the more time your money has to grow.
Managing Debt Effectively
While some debt, such as a mortgage or student loans, can be a normal part of life, managing it responsibly is essential for long-term financial success. High-interest debt, like credit card balances, can hinder your financial progress.
Strategies for Paying Off Debt
- Debt Snowball Method: Start by paying off the smallest debt first while making minimum payments on others. Once the smallest debt is paid off, move on to the next one. This method helps build momentum and motivation.
- Debt Avalanche Method: Focus on paying off the debt with the highest interest rate first. This method saves you money on interest in the long run, though it may take longer to see progress.
- Consolidation and Refinancing: If you have multiple high-interest debts, consider consolidating them into a single loan or refinancing to lower your interest rates.
- Avoiding New Debt: While paying off existing debt, avoid accumulating new debt. Stick to your budget, use credit responsibly, and consider limiting your use of credit cards.
Investing for Long-Term Growth
Investing is one of the most effective ways to build wealth over time. By putting your money into assets that grow in value, you can significantly increase your net worth and achieve long-term financial success.
The Power of Compound Interest
One of the main reasons investing is so powerful is compound interest. This is the process by which you earn interest not only on your initial investment but also on the interest your investment has already generated. The earlier you start investing, the more time your money has to grow exponentially.
Investment Vehicles
When it comes to investing, there are various vehicles you can use, depending on your risk tolerance, time horizon, and goals:
- Stocks: Stocks offer high potential returns but come with higher risk. Consider diversifying your stock portfolio to reduce risk.
- Bonds: Bonds are lower-risk investments that pay fixed interest over time. They’re suitable for conservative investors looking for steady income.
- Mutual Funds and ETFs: These funds pool money from many investors to invest in a diversified portfolio of stocks, bonds, or other assets.
- Real Estate: Investing in property can provide both income (through rental properties) and capital appreciation.
Retirement Accounts
Retirement accounts, such as a 401(k), IRA, or Roth IRA, are specifically designed to help you save for retirement. These accounts offer tax advantages, which can significantly boost your savings over time.
Planning for Retirement
Retirement planning is an essential aspect of personal finance. Ensuring that you have enough money to support yourself during your retirement years requires discipline and foresight.
How Much Do You Need to Save?
The amount you need to save for retirement depends on factors such as your desired lifestyle, estimated expenses, and the age at which you plan to retire. A common rule of thumb is to aim for 70-80% of your pre-retirement income to maintain a similar standard of living.
Start Early
The earlier you start saving for retirement, the better. Thanks to compound interest, even small contributions can grow significantly over time. Contribute regularly to your retirement accounts, and take advantage of employer matching contributions if available.
Monitoring Your Financial Health
Achieving long-term success in personal finance requires ongoing monitoring of your financial health. Regularly review your budget, savings, investments, and debt to ensure you’re on track to meet your goals.
Track Your Net Worth
Your net worth is the difference between your assets (what you own) and liabilities (what you owe). Tracking your net worth allows you to see your progress and identify areas for improvement.
Adjust Your Strategy as Needed
Life circumstances change, and your financial strategy should evolve accordingly. Whether it’s a change in income, family situation, or financial goals, be flexible and adjust your plan as needed to stay on track.
Conclusion
Mastering personal finance is not a one-time event but a continuous process. By setting clear financial goals, creating a realistic budget, saving consistently, managing debt effectively, and investing for the future, you can pave the way for long-term financial success. With discipline, patience, and the right strategies, you’ll be well on your way to achieving financial independence and enjoying a secure, prosperous future.